Online Investigation of Terrorist Threats: Techniques, Tools, and Real-World Examples
In today’s interconnected world, terrorist organisations exploit the digital landscape to spread propaganda, recruit members, and coordinate attacks. For investigators, identifying and mitigating these threats online is critical but highly challenging. In this blog, we explore the methods and tools used in online investigations and highlight real-world examples from news reports to provide practical insights into this crucial field.
The Legal and Ethical Framework
Before delving into investigative techniques, it is essential to consider the legal and ethical implications. Investigators must comply with data protection laws, such as the UK’s Data Protection Act 2018, and work within the boundaries of anti-terrorism legislation, such as the Terrorism Act 2006. Any collection or analysis of data must prioritise public safety while respecting individual rights to privacy.
UK Terrorism Prevention Strategies and Threat Levels
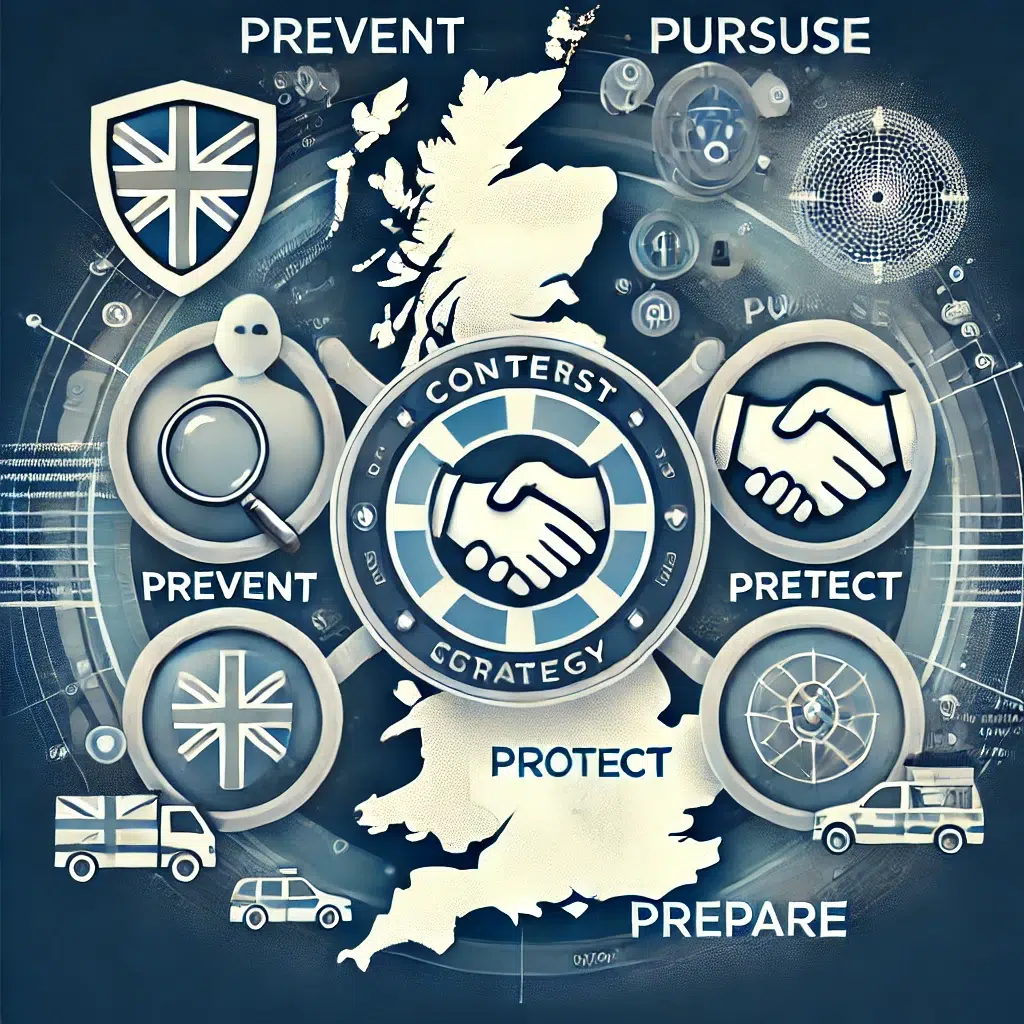
1. UK Counter-Terrorism Strategies
The UK employs a multi-faceted approach to prevent terrorism through the CONTEST Strategy, which includes four key pillars:
- Prevent: Stopping people from becoming terrorists or supporting terrorism by addressing radicalisation.
- Pursue: Disrupting terrorist activity and bringing perpetrators to justice.
- Protect: Strengthening the UK’s defences against terrorist attacks, such as safeguarding public spaces and infrastructure.
- Prepare: Enhancing the ability to respond effectively to terrorist incidents and mitigate their impact.
More information about the CONTEST Strategy can be found on the UK Government’s website.
2. UK Terrorism Threat Levels
The UK’s terrorism threat levels are set by the Joint Terrorism Analysis Centre (JTAC) and reflect the likelihood of a terrorist attack:
- Low: An attack is highly unlikely.
- Moderate: An attack is possible but not likely.
- Substantial: An attack is likely.
- Severe: An attack is highly likely.
- Critical: An attack is highly likely in the near future.
As of [insert current date], the UK’s threat level is [current threat level]. Threat levels are reviewed regularly and can be checked on the MI5 website.
Techniques for Online Investigations
1. Open Source Intelligence (OSINT)
OSINT involves gathering publicly available information from the internet. Investigators use this method to monitor social media, forums, and blogs where extremists may share content.
- Example: In 2020, UK authorities foiled a far-right terrorist plot after identifying discussions in online forums promoting violence. The investigation relied on analysing user interactions on platforms like 4chan and Telegram. Read more here.
Key Tools:
- Maltego: Helps map relationships between individuals, organisations, and digital assets.
- Spiderfoot: An OSINT automation tool that gathers and analyses data from multiple sources.
- Shodan: Useful for identifying internet-connected devices that may be exploited in cyberattacks.
2. Social Media Monitoring
Terrorist groups often use mainstream social media platforms for recruitment, propaganda dissemination, and coordination. Investigators monitor hashtags, groups, and accounts for extremist content and activities.
- Example: After the Manchester Arena bombing in 2017, investigators traced the attacker’s online activity, including Twitter and Facebook posts, to uncover his links to ISIS-affiliated networks. More details here.
Key Tools:
- TweetDeck: For monitoring multiple Twitter accounts or hashtags simultaneously.
- CrowdTangle: Tracks trends and the spread of content across social media.
- SocioSpy: Explores public social media profiles to identify connections.
3. Dark Web and Encrypted Platforms
Many terrorist activities have migrated to the Dark Web and encrypted messaging platforms to evade detection. Investigators access these hidden areas of the internet using specialised tools and techniques.
- Example: In 2022, Europol dismantled a major terrorist financing network operating through Dark Web marketplaces. Investigators traced cryptocurrency transactions and communications on platforms like Tor. Full story here.
Key Tools:
- Tor Browser: For accessing Dark Web sites.
- CipherTrace: Analyses cryptocurrency transactions linked to illicit activities.
- HTTrack: Mirrors Dark Web sites for offline analysis.
4. Language and Sentiment Analysis
Analysing language patterns and sentiment in online posts can help detect radicalisation and predict escalation. Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools assist in identifying threatening or inciting content.
- Example: In 2021, MI5 flagged a series of posts written in Arabic on an extremist blog. The analysis revealed coded messages outlining potential targets, leading to the prevention of a planned attack. More information.
Key Tools:
- Google Translate or DeepL: For translating foreign-language content.
- Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK): For sentiment and keyword analysis.
- Hootsuite Insights: Tracks trends in online discourse.
Indicators of Terrorist Threats
While monitoring online spaces, investigators look for specific indicators that may signal terrorist activities:
- Radicalised Content: Posts endorsing violence or extremist ideologies.
- Recruitment Efforts: Attempts to enlist members or solicit donations.
- Operational Planning: Discussions about weapons, targets, or timelines.
- Geotagged Content: Photos or posts revealing sensitive location data.
Collaboration and Reporting
Effective investigation often requires collaboration between governments, law enforcement agencies, and technology companies. Platforms such as Google, Meta, and Twitter have implemented policies to identify and remove extremist content. However, investigators must also report findings to counter-terrorism units or organisations like Europol for cross-border threats.
- Example: In 2019, YouTube removed hundreds of videos linked to ISIS after researchers flagged the content. The swift action helped disrupt propaganda efforts targeting Western audiences. Read the report.
Challenges in Online Investigations
Despite the availability of tools and techniques, investigators face significant hurdles:
- Encryption and Anonymity: End-to-end encryption on platforms like WhatsApp and Signal can hinder monitoring efforts.
- Volume of Data: The sheer scale of online content requires advanced AI-driven tools to filter and analyse data efficiently.
- False Positives: Misidentification of innocent users or misinterpretation of content can lead to serious repercussions.
Conclusion
Online investigations of terrorist threats are an essential component of modern counter-terrorism efforts. By leveraging advanced OSINT tools, monitoring social media, and accessing hidden parts of the internet, investigators can identify and disrupt threats before they materialise. However, these efforts must balance efficacy with ethical considerations to ensure public safety and individual rights.
The digital battlefield is ever-evolving, and so too must our strategies for combating terrorism online. By learning from past examples and investing in cutting-edge technology, we can continue to protect our societies from those who seek to harm them.